PHP Lessons - Lesson 2 - Working with files: opening, writing, reading.
In the previous lesson, we built the framework for our guestbook, blog, or chat application. Now it’s time to add functionality. In this lesson, we’ll save entries to files and display entries from those files.
PHP has many functions for file operations. We’ll look at a few of them. Most likely, your website will store data in a database (I’m sure of that) rather than in files. So we’ll just touch on the basics here to give you an understanding. We'll cover working with databases later.
If you don’t have the files from the last lesson, go back and download them first.
PHP Lessons - Lesson 3 - Working with MySQL DB.
You might think it’s too early to begin the third lesson with working in MySQL. But trust me, it’s not. Learning PHP as a web programming language without learning how it interacts with databases is like having a computer without internet. Yes, you can work on such a computer, but you won’t be able to get information. So let’s grit our teeth and start writing SQL queries, even if we know nothing about the SQL language yet.
PHP Lessons - Lesson 3.1 - Working with MySQL DB. Creating tables.
In the previous lesson, we created a connection to the database. In this lesson, we’ll create tables for our future website. First, let’s add the name of the required database in the simpleCMS class:
PHP Lessons - Lesson 3.2 - Working with MySQL DB. Inserting data INSERT INTO. Selecting data SELECT
In the previous lesson, we created a table for our website. In this lesson, we will improve the table and start working with the database: adding and retrieving data from it. I don’t think anything too difficult is coming up, so let’s begin.
First, I suggest we improve our messages table. Right now it has fields for the data, but it needs an extra column for numbering records. If you look at the Drupal database, the node table has a nid field for this purpose. We’ll do something similar with our messages table.
PHP Lessons - Lesson 3.3 - Working with MySQL DB. Updating data UPDATE.
We have already learned MySQL operators like SELECT and INSERT INTO. Now it's time to learn how to update existing data in the database using the SQL UPDATE operator. But first, let's modify our index.php file and add a new route. Find this code:
if ($_GET['admin'] == 1) {
print $obj->display_admin();
} else {
print $obj->display_public();
}
And replace it with the following code:
PHP Lessons - Lesson 3.4 - Working with MySQL DB. DELETE Deletion Queries.
In the previous lesson, we learned how to add new methods to our management class simpleCMS. Now let’s add one more method to delete a record: delete().
We’ll add the method as usual:
public function delete($mid) {
}
As you can see, we pass a parameter $mid – the ID of our record. If you recall the previous lesson, we used a different approach to pass the parameter via a GET request. This time we’ll try passing the parameter another way.
PHP Lessons - Lesson 3.5 - Working with MySQL DB. JOIN operator. Uploading files to the server.
Before I started writing this lesson, I thought for a long time about the best way to present queries using the JOIN operator. The point is that the JOIN operator is used to retrieve data from multiple tables at once. And since we need another table, let's create one. I suggest creating a table for files, which we will upload through a form in this lesson. This way, the lesson will combine two directions: working with databases and working with forms.
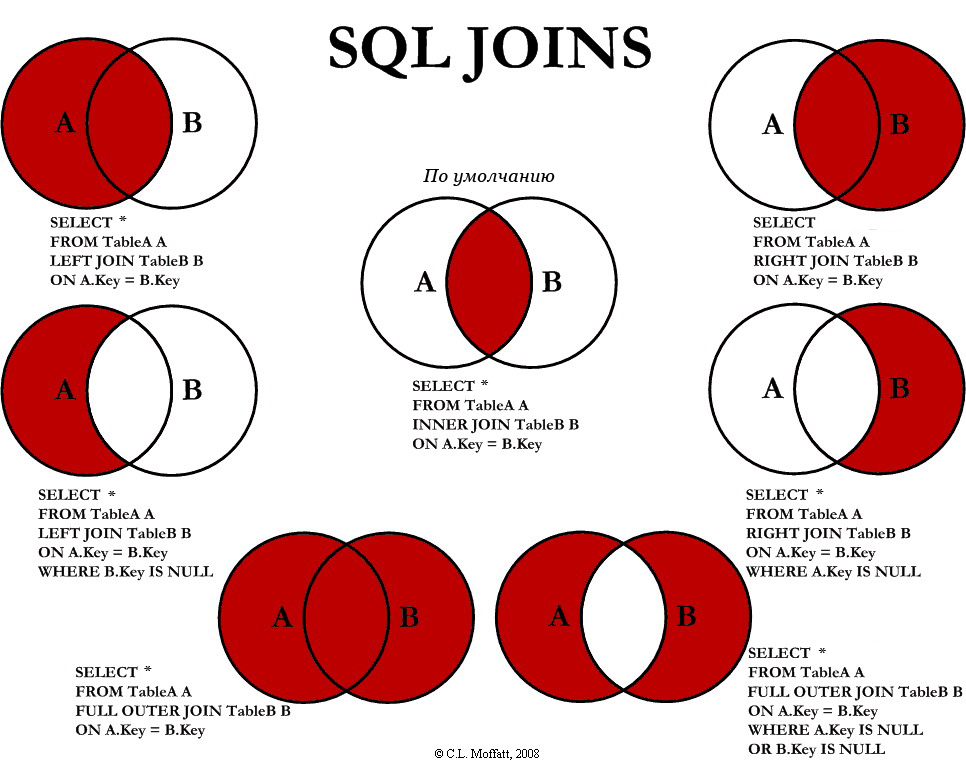
PHP Lessons - Lesson 3.6 - Working with MySQL DB. Types of JOIN operator.
In MySQL, JOIN queries can be written in several different ways. We'll try to cover all of them. Here's a list of JOIN query types:
- INNER JOIN
- LEFT JOIN
- LEFT JOIN without matches in the right table
- RIGHT JOIN
- RIGHT JOIN without matches in the left table
- FULL OUTER JOIN
- FULL OUTER JOIN where the left or right table is empty
Here’s an illustration of these types of JOINs:
PHP Lessons - Lesson 4 - Working with Images, GD2 Library
In the previous lessons, we learned how to write database queries, so now we'll focus less on writing queries and more on practicing them. We'll also combine writing queries with learning other PHP features, starting with image processing. In one of the previous lessons, we already uploaded files and even created a Files table for uploaded files. Now, let’s upload images to the same table. But first, we need to add a photo upload field to the content creation form.
PHP Lessons - Part 3 - Creating Your Own CMS
Creating websites on CMS platforms is not limited to Drupal, Joomla, and WordPress. In fact, most websites in the world are built on custom CMS solutions. Even though a lot of PHP code has already been written, developers often prefer to use their own tools. Let’s try to understand why you might want to build your own CMS.